INTRODUCTION
Children born to obese parents have a high rate of becoming obese and have a high probability of developing various diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and high blood pressure. It is known that excessive nutritional intake of the mother affects abnormal neural circuit growth in the fetus and changes in the sensitivity of leptin in the hypothalamus, which impairs the viability of progenitor cells in the hippocampus, thereby reducing the neuronal cell production of the fetus (Chang et al., 2008). Radial 8-arm maze test is behavior test to detect spatial learning memory. Radial 8-arm maze test revealed impairment of spatial learning memory in traumatic brain injury rats. Meanwhile, treadmill exercise showed alleviation of traumatic brain injury-induced impairment of spatial learning memory in rats (Ko et al., 2019).
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer (NF-κB) is a main transcription factor of macrophages and induces several inflammatory genes, such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-1β, and IL-6 (Jeong et al., 2017). NF-κB is a protein complex that controls the transcription of DNA, cytokine production, and cell survival. NF-κB is associated with synaptic plasticity and memory process (Albensi and Mattson, 2000; Meffert et al., 2003). Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha (IκB-α) is a member of the cellular protein family that functions to repress the NF-κB transcription factor.
B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) family is divided into antiapoptotic protein and proapoptotic protein according to their functions, and then determines the mitochondrial response to apoptosis stimuli (Upadhyay et al., 2003). Bcl-2 can inhibit apoptosis by inhibiting cytochrome c release from mitochondria. However, Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL form heterodimers with the major proapoptotic member Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax) and lose their ability to function as a preventative (Kuwana and Newmeyer, 2003). Activation of caspases is the other important feature of apoptosis, and caspase-3 is a key performer of apoptosis (Song et al., 2018).
Proteins of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family are implicated in many physiological processes and also implicated in pathological processes such as arthritis, intracerebral hemorrhage, and metastasis in the brain (Vandooren et al., 2013; Wang and Tsirka, 2005). MMP-9 performs many functions including degradation of extracellular matrix, activation of IL-1β, and cleavage of several chemokines (Opdenakker et al., 2001).
In this experiment, the memory state of rat pups born to old and obese mother rats and the effect of a treadmill running of mother rats on the memory of rat pups were studied. The radial 8-arm maze test was performed to detect spatial learning memory, and the level of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in hippocampus was measured by enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA). Western blotting was performed for the expression of NF-κB, IκB-α, Bax, Bcl-2, MMP-9, and immunohistochemistry for caspase-3 was conducted.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals and classification
This experiment was reviewed by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Kyung Hee University and acquired the approval number as follows: KHUASP (SE)-20-135. Old female rats were fed a normal diet (5% of fat), and old and obese female rats were fed a high fat diet (60% of fat). For mating, at 46 weeks in age, Sprague-Dawley male rats (15-week-old) were reared in the same cage for 7 days at the ratio of one female and two males. Female rats were divided into two groups: one group is old mother rats (n=8) and the other group is old and obese mother rats (n=8). Treadmill running was conducted for a total of 23 weeks, including 20 weeks before and 3 weeks of pregnancy. Exercise load was at a speed of 5 m/min for 20 min per day. The newborn rats were classified into following groups (n=10): pups born to old mother rats, pups born to old mother rats with exercise, pups born to old and obese mother rats, and pups born to old and obese mother rats with exercise.
Radial 8-arm maze test
The radial 8-arm maze test was used to detect spatial learning memory as explained below (Ko et al., 2019). The radial arm maze device consists of a central octagonal plate and eight radial arms 35 cm long and 8 cm wide, placed 1 m above the floor. Cups 3 cm in diameter and 1 cm deep were placed at the ends of eight radiating arms. The rat pups were trained 3 times prior to measuring spatial learning memory. Water was forbidden for 24 hr during training, and water was allowed to drink when found in the cup at the end of the eight radiating arms. The time it took to find the water in the cups was calculated, and the error was calculated for re-entering the arms that had already been entered, and the number of correct choices until the first error occurred was calculated. The experiment ended when the rats found water in all eight arms, or more than 8 min had passed.
Enzyme-linked immunoassay
ELISA was done to measure the level of proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, as explained Ko et al. (2020). Enzyme immunoassay kit (Abcam, Cambridge, UK) was used in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
Western blot
Western blot analysis for NF-κB, IκB-α, Bax, Bcl-2, MMP-9 expression was used as explained below (Ko et al., 2020; Park et al., 2020). Hippocampal tissues were lysed in a lysis buffer containing 150 mM NaCl, 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH, 7.5), 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 100-mg/mL leupeptin, 1% Nonidet P40, 0.5% deoxycholic acid, 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate. Rabbit NF-κB antibody (1:1,000; Abcam), rabbit IκB-α antibody, rabbit phosphorylated IκB-α (p-IκB-α) antibody (1:1,000; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA), rabbit MMP antibody (1:2,000; Cell Signaling Technology, Inc., Danvers, USA), mouse Bax antibody, mouse Bcl-2 antibody, and β-actin antibody (1:1,000; Santa Cruz Biotechnology) were used as the primary antibodies. Horseradish peroxidase-conjugated anti-mouse antibody (1:2,000; Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA, USA) for β-actin, Bax, Bcl-2, and horseradish peroxidase-conjugated anti-rabbit antibody (1: 2,000; Vector Laboratories) for NF-κB, IκB-α, and MMP were used as the secondary antibodies. Image-Pro Plus computer-aided image analysis system (Media Cybernetics Inc., Silver Spring, MD, USA) was used for band quantification.
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry for capsase-3 was done as explained below (Hwang et al., 2019; Lee et al., 2020). The sections were treated with mouse anti-caspase-3 antibody (1:500; Santa Cruz Biotechnology) overnight. The sections were treated with the biotinylated mouse secondary antibody for another 1 hr. The bound secondary antibody was then amplified using a Vector Elite ABC kit (1:200; Vector Laboratories).
RESULTS
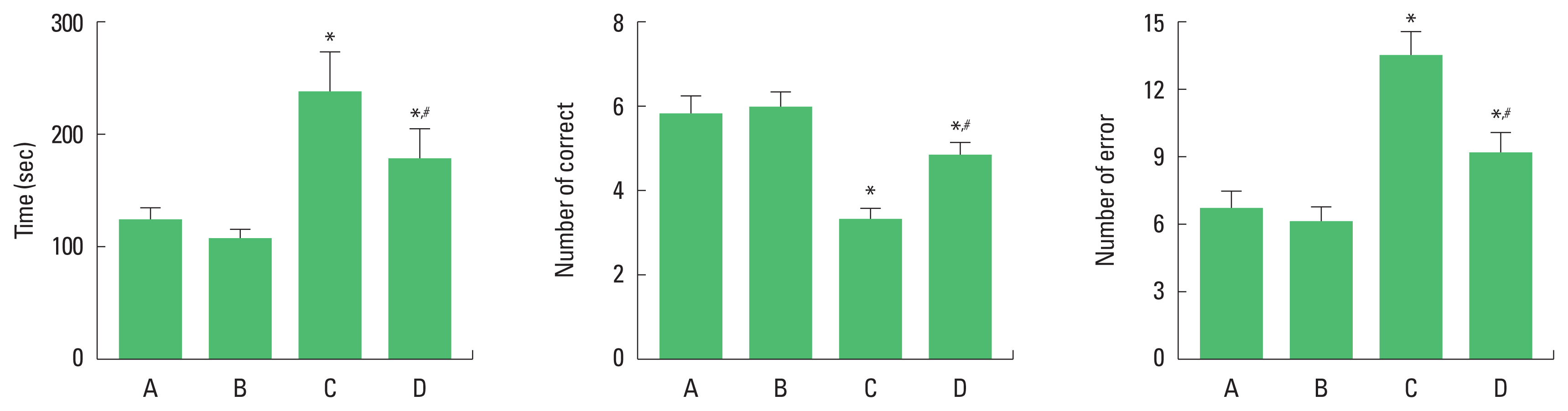
Spatial learning memory
The time to completion was increased, the number of correct choices was decreased, and the number of error choices was increased in the pups born to old and obese mother rats compared to the pups born to old mother rats. In contrast, pups born to old and obese mother rats with exercise showed decreased completion time, increased correct choice number, and decreased error choice number (Fig. 1).
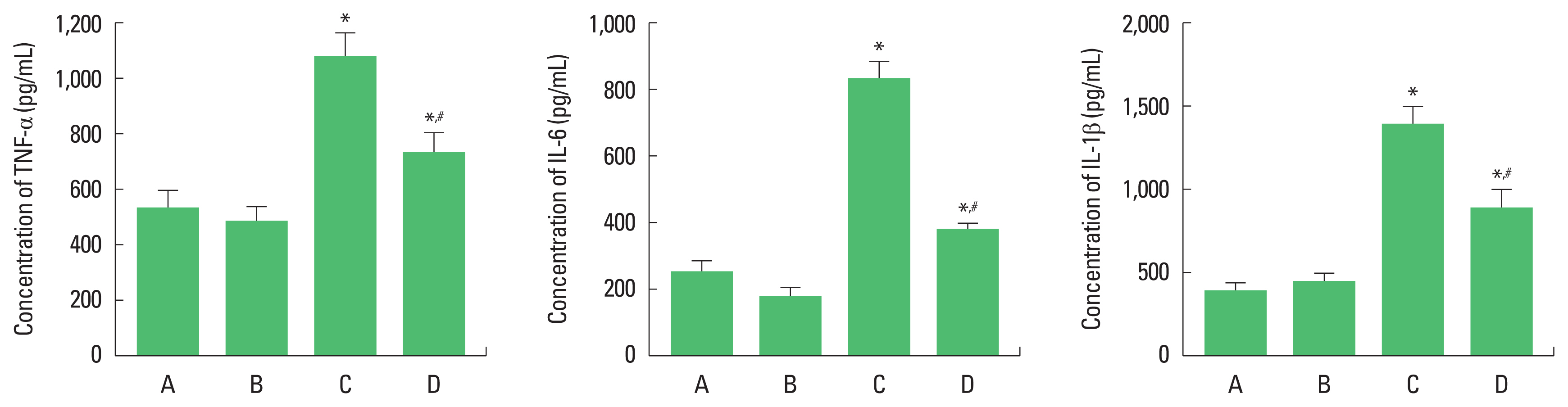
Proinflammatory cytokines
Concentration of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β in the hippocampus was increased in the pups born to old and obese mother rats compared to the pups born to old mother rats. In contrast, pups born to old and obese mother rats with exercise showed suppressed TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β level (Fig. 2).
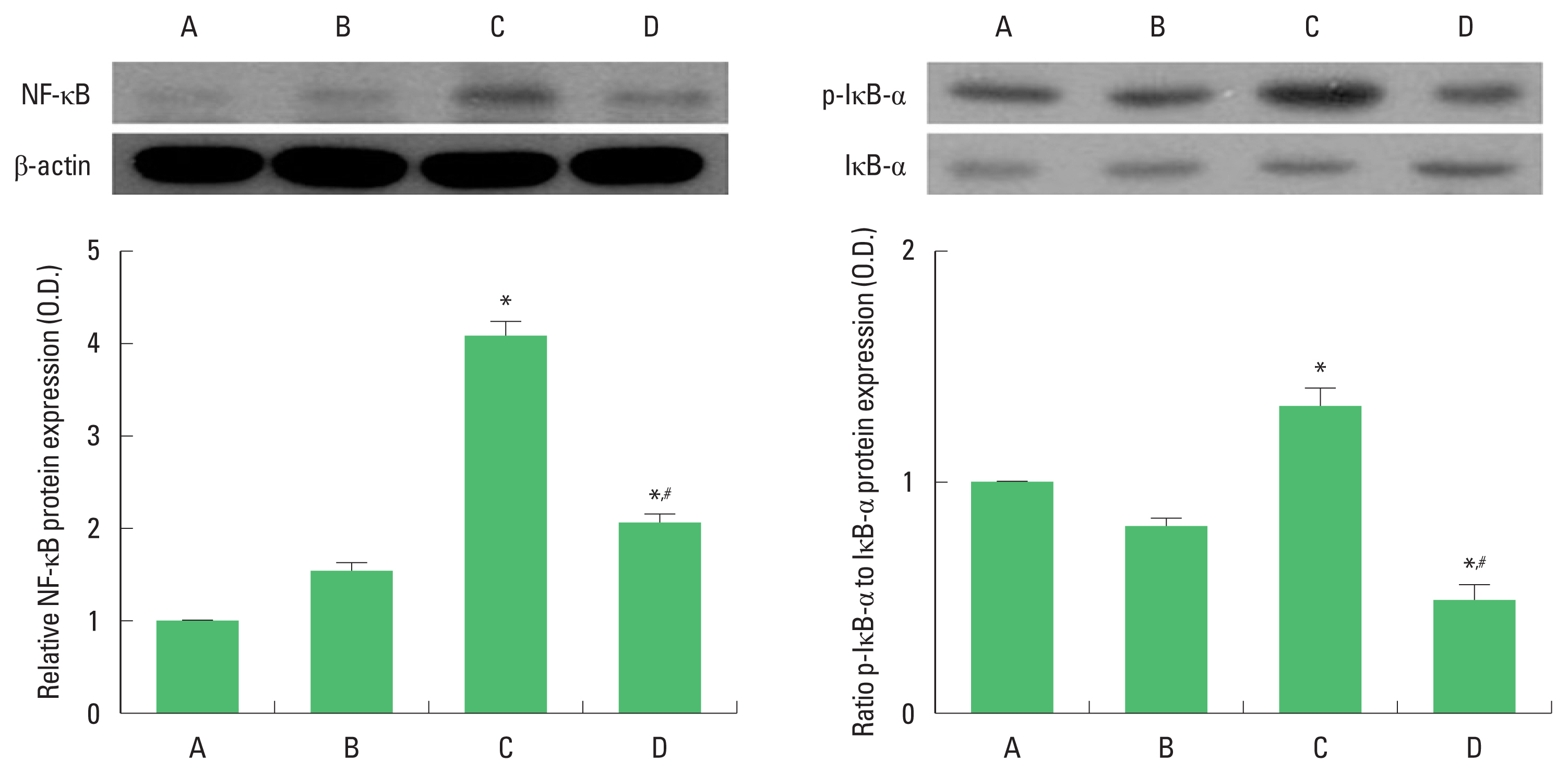
NF-κB expression and p-IκB-α to IκB-α ratio
Expression of NF-κB and ratio of p-IκB-α to κB-α in the hippocampus was increased in the pups born to old and obese mother rats compared to the pups born to old mother rats. In contrast, pups born to old and obese mother rats with exercise showed suppressed NF-κB expression and p-IκB-α to κB-α ratio (Fig. 3).
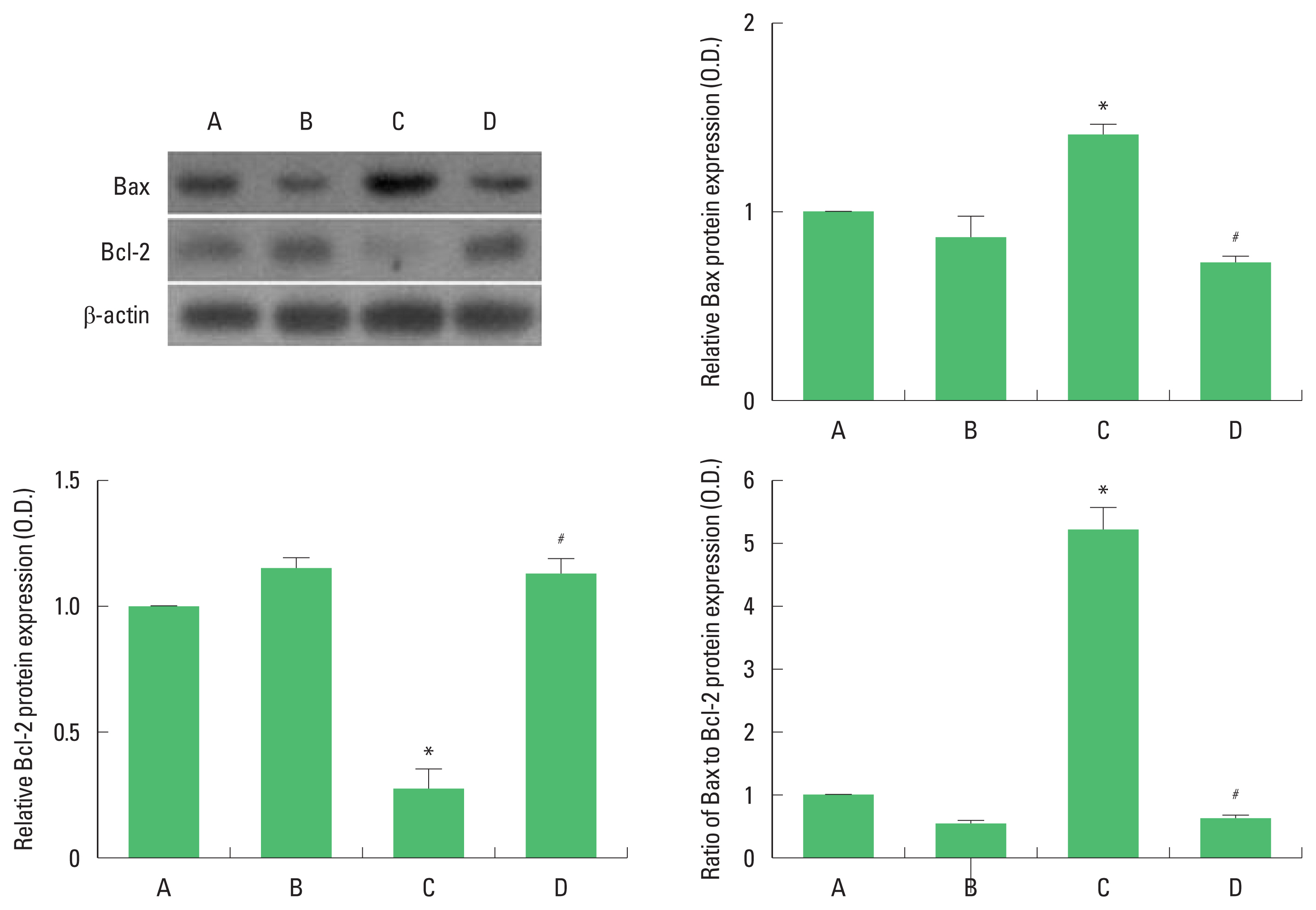
Bax and Bcl-2 expression
Expression of Bax in the hippocampus was increased and expression of Bcl-2 was decreased, resulting in enhanced Bax to Bcl-2 ratio in the pups born to old and obese maternal rats compared to the pups born to old mother rats. In contrast, pups born to old and obese mother rats with exercise showed suppressed Bax expression and enhanced Bcl-2 expression, resulting in suppressed Bax to Bcl-2 ratio (Fig. 4).
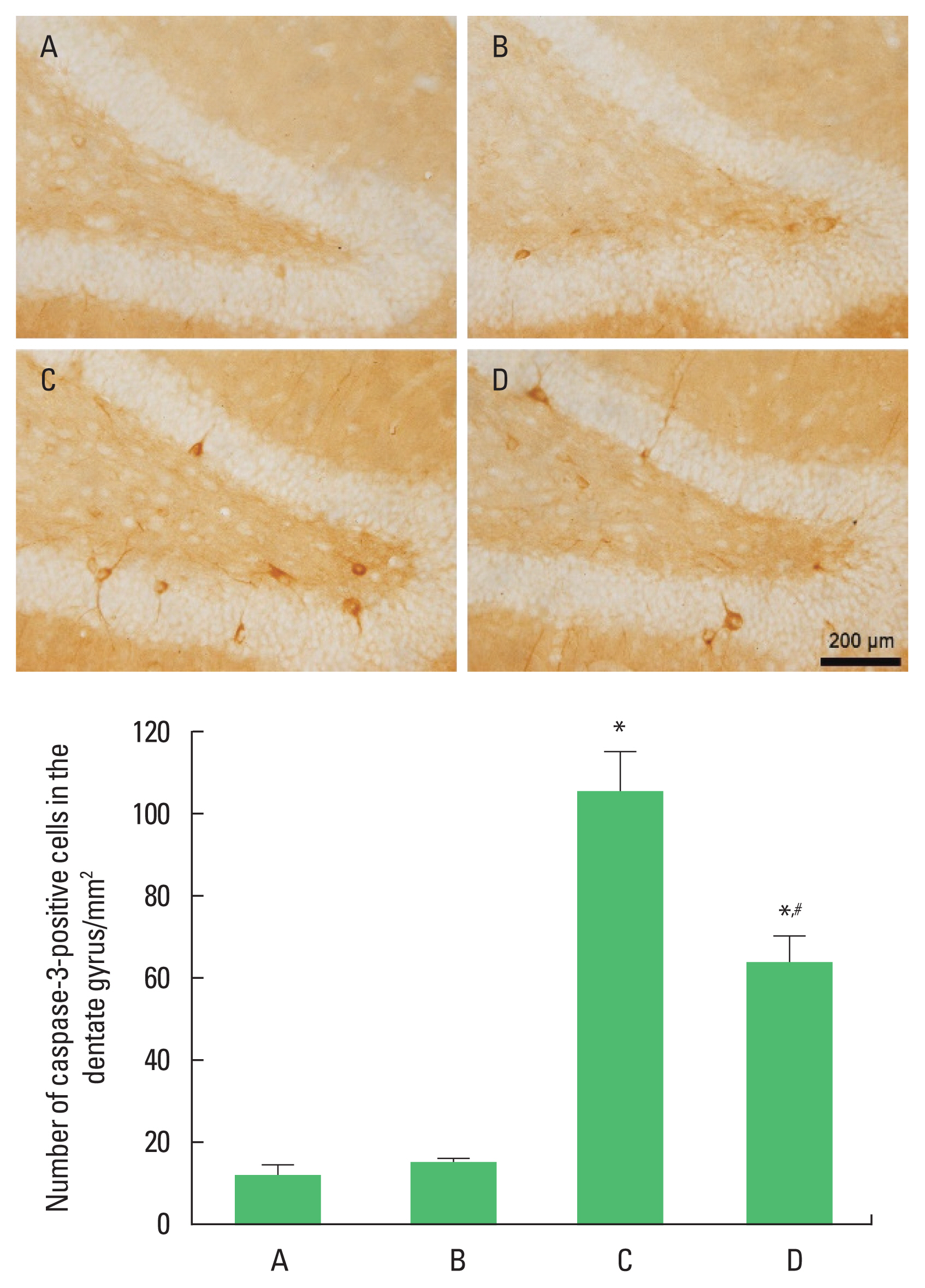
Caspase-3 immunohistochemistry
The number of caspase-3-positive cells in the hippocampal dentate gyrus was increased in the pups born to old and obese mother rats compared to the pups born to old mother rats. In contrast, pups born to old and obese mother rats with exercise showed suppressed caspase-3-positive cell number (Fig. 5).
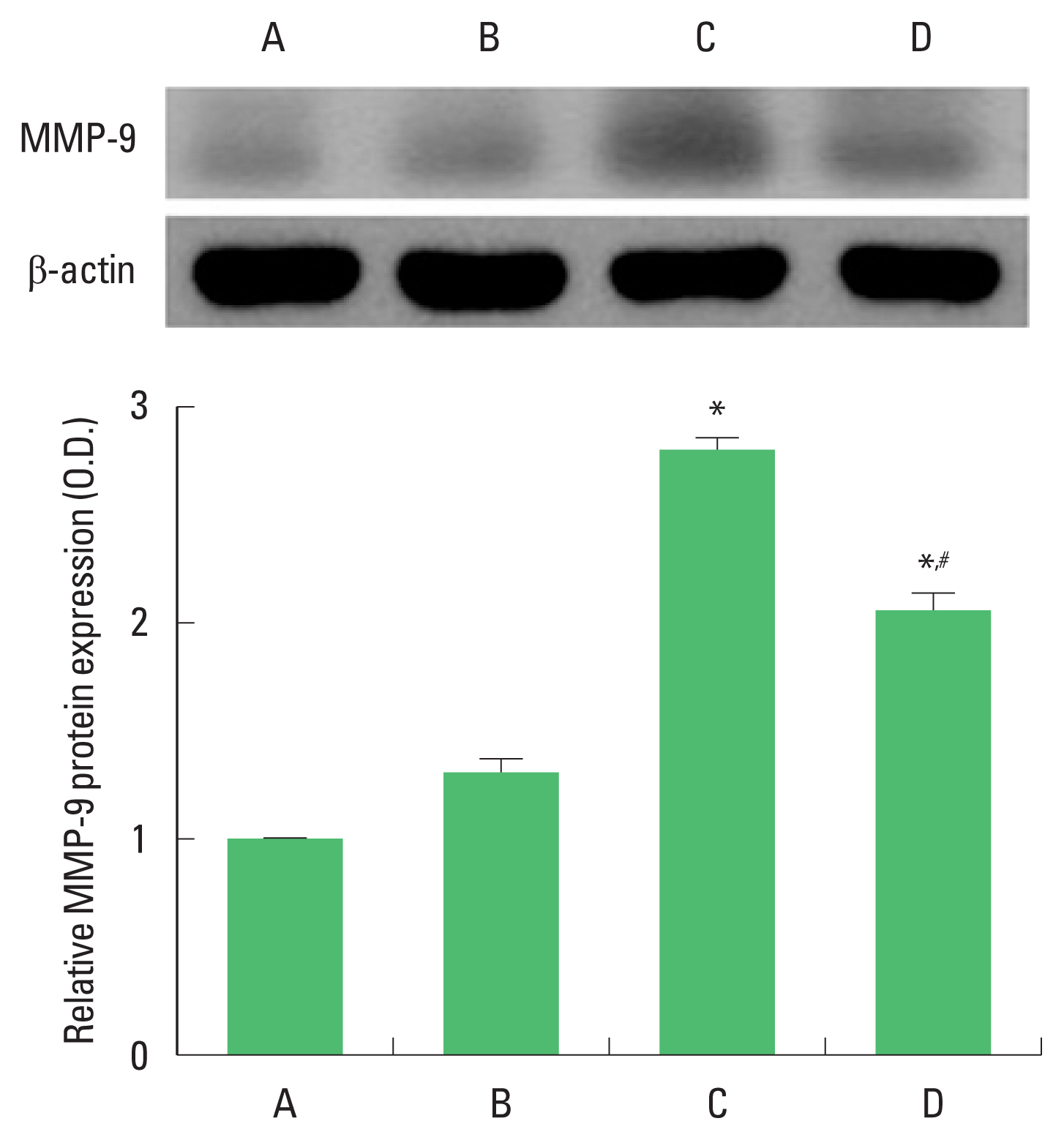
MMP-9 expression
Expression of MMP-9 in the hippocampus was increased in the pups born to old and obese mother rats compared to the pups born to old mother rats. In contrast, pups born to old and obese mother rats with exercise showed decreased MMP-9 expression (Fig. 6).
DISCUSSION
Memory exercise, healthy eating, fitness and stress reduction can improve cognitive function and brain efficiency (Small et al., 2006). Spatial learning memory was aggravated by traumatic brain injury, but treadmill exercise improved memory impairment due to traumatic brain injury through upregulation of dopamine level and downregulation of dopamine receptor expression (Ko et al., 2019). In this result, spatial learning memory was decreased in the pups born to old and obese mother rats, however exercise of mother rats ameliorated spatial learning memory impairment of the pups born to old and obese mother rats. These results mean that maternal exercise improved spatial learning memory in the rat pups born to old and obese mother rats.
Enhanced secretion of proinflammatory cytokines (including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6) attributed to the damaging effect of indomethacin on gastric mucosa, and reduction of proinflammatory cytokines promoted recovery of gastric injury (Ko et al., 2020). In this result, the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, was increased in the pups born to old and obese mother rats, however exercise of mother rats suppressed the production of proinflammatory cytokines of the pups born to old and obese mother rats. These results mean that maternal exercise suppressed exacerbation of inflammation in the rat pups born to old and obese mother rats.
NF-κB is consistently active in arthritis, asthma, atherosclerosis, gastritis, inflammatory bowel disease, sepsis, and others (Monaco et al., 2004). In obesity and aging, NF-κB was highly expressed and anti-inflammatory level was reduced (Kauppinen et al., 2013). In this result, NF-κB expression and IκB-α phosphorylation were increased in the pups born to old and obese mother rats, however exercise of mother rats suppressed NF-κB expression and IκB-α phosphorylation of the pups born to old and obese mother rats. These results mean that maternal exercise suppressed inflammation inducer in the rat pups born to old and obese mother rats
Overexpressing Bax represents initiation of apoptosis (Lee et al., 2020; Song et al., 2018). Upon activation of Bax, apoptosis resumes with the consumption of Bcl-2 in complex with Bax (Dlugosz et al., 2006). Expression of Bax was enhanced, while expression of Bcl-2 was suppressed in the old rats that underwent social isolation, which facilitated apoptosis. Meanwhile, swimming inhibited Bax expression and increased Bcl-2 expression, resulting in suppression of apoptosis (Park et al., 2020). In this result, Bax expression was enhanced and Bcl-2 expression was suppressed, resulting in Bax to Bcl-2 ratio was increased in the pups born to old and obese mother rats. However, exercise of mother rats decreased Bax expression and increased Bcl-2 expression, resulting in Bax to Bcl-2 ratio was suppressed in the pups born to old and obese mother rats. These results mean that maternal exercise exerted suppressive tendency on apoptosis in the rat pups born to old and obese mother rats
Caspase-3 is one of the caspases responsible for the final trigger of apoptosis (Lee et al., 2020). Expression of caspase-3 in the hippocampus was increased in the rats of the social isolation group compared to the control rats. However, treadmill exercise decreased caspase-3 expression in the social isolation rats (Song et al., 2018). In this result, the number of caspase-3 was increased in the pups born to old and obese mother rats, however exercise of mother rats suppressed the number of caspase-3 of the pups born to old and obese mother rats. These results mean that maternal exercise inhibited apoptosis in the rat pups born to old and obese mother rats.
MMP-9 is implicated in the development of aortic aneurysms and doxycycline inhibits aortic aneurysm growth through inhibition of MMP-9 (Lindeman et al., 2009). MMP-9 level was increased with the progression of idiopathic atrial fibrillation (Li et al., 2014). MMP-9 plays a pivotal role in angiogenesis, stromal remodeling, and metastasis (Farina and Mackay, 2014). In this result, the level of MMP-9 was increased in the pups born to old and obese mother rats, however exercise of mother rats suppressed the level of MMP-9 of the pups born to old and obese mother rats. These results mean that maternal exercise inhibited inflammatory reaction in the rat pups born to old and obese mother rats
In this study, the spatial learning memory of pups born to old mother rats was not significantly affected by the maternal exercise. However, the spatial learning memory of pups born to old and obese mother rats was significantly affected. Spatial learning memory was impaired through NF-κB activation in pups born to old and obese mother rats. However, when exercise of mother was performed, the impairment of spatial learning memory in pups was ameliorated. Therefore, it can be seen that exercise during pregnancy of older and obese mothers is an important factor in fetal health management.